Electrospinning and electrospraying are electrohydrodynamic processes wherein a polymer solution is used to fabricate fibers or particles, respectively. In the most basic setup, a polymer solution is loaded into a syringe, and it flows through a capillary tube where a high voltage is applied, and the liquid is ejected towards a collector. Depending on the solution properties, fibers or particles are generated during the process.
It is common for many research labs to build their own electrospinning or electrospraying system, often driven by the passion for innovation and application needs. However, home-built systems are usually plagued by safety issues and have several limitations including inconsistencies in fiber/particle morphology and limited scalability.
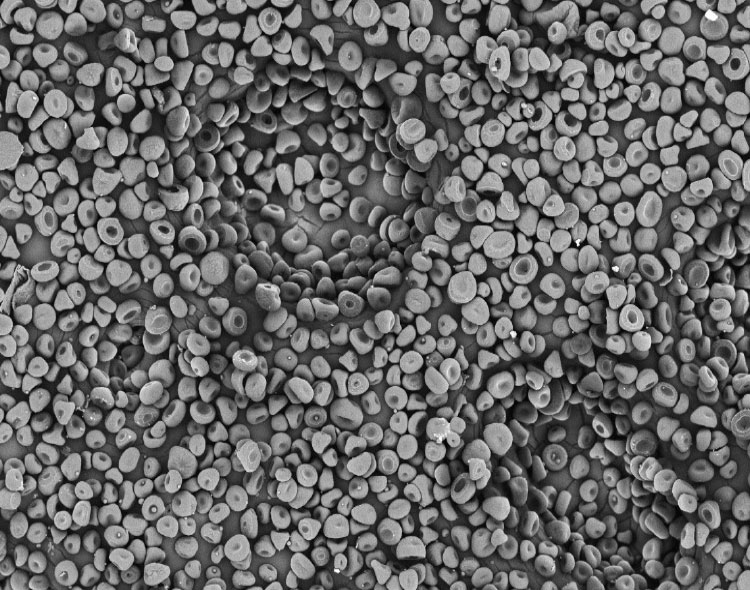

Several different commercial electrospinning and electrospraying instruments are available that offer significant benefits to users. Some of the reasons to consider buying a commercial system instead of building your own home-engineered system include:
1. Environmental Control
Since electrospinning and electrospraying are affected by the evaporation rate of the solvent, controlling the environmental parameters during the fabrication process, especially relative humidity (RH) and temperature (T), are critical to ensure consistency and repeatability. In the case of very low RH, the solvent could evaporate too quickly, clogging the needle and disrupting the process. Commercial units are capable of tightly controlling temperature and relative humidity, with ranges around 18-45°C and 10-80%, respectively. Some commercial units are even able to control airflow to help with solvent evaporation.
2. Precision and Consistency
Commercial electrospinning/electrospraying equipment is designed and engineered with high precision and built with components that work seamlessly with each other, ensuring consistent and repeatable results. Each machine undergoes rigorous factory assessment tests (FAT) to prevent uncertainties that usually come with home-built systems. Commercial systems offer site assessment tests (SAT), installation qualification (IQ), operational qualification (OQ), and product qualification (PQ). These can be critical when fibers and particles must be fabricated under current good manufacturing processes (cGMP).
3. Safety Features
Commercial electrospinning and electrospraying systems are designed with safety features that protect the users and the equipment. Generally, commercial systems are housed in an enclosure with an interlock system to deactivate all processing parameters when the door is opened. Safety features, such as a ventilation system to remove any hazardous solvents, built-in alarms, emergency shutoff, and a nitrogen gas environment with oxygen sensors during flammable solvents use, are also available in commercial instruments. Home-built units lack most of these safety features, exposing users to high voltages, solvent vapors, or even explosions.

4. Accessories
Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques are used in a wide spectrum of applications. Based on the application needs, different accessories might be necessary. For example, a secondary syringe pump might be required to fabricate coaxial structures, a multi-needle setup may be useful to increase throughput, and a high-speed rotating collector may facilitate aligned fiber production. Some applications may require the simultaneous processing of two different solutions with independent parameter controls. Beneficially, commercial units typically offer over 20+ accessories that can be integrated into the basic system to accommodate a variety of application needs.
5. Automation & Software
Commercial electrospinners and electrosprayers typically include robust software controls to set and adjust the parameters needed to fine-tune the fabrication process. Automated routines and recipe-based fabrication processes are also commonly available on these systems. Process data hubs and built-in sensors can provide real-time feedback, thereby aiding with monitoring the process and machine parameters. All these lead to a better understanding of the fabrication process and ensure consistency between batches.
6. Upgradable and Scalable
Although both electrospinning and electrospraying are scalable techniques, most home-built systems are not scalable and are usually limited to one emitter. While these are sufficient early in the development phase, they soon become inadequate when higher throughput fabrication of fibers or particles is desired. A system that has more features and throughput capabilities might be needed as the project develops or applications mature. Commercial systems are designed with scalability in mind, allowing the user to upscale their process. Entry-level systems are generally equipped with only one to a few needles while higher-end models used in productions-level fabrication may be equipped with more than 5000 needles and with productivity of up to 12 kg/h of dry fibers (depending on solution).
7. Customization
Emerging applications often require customization of the electrosprayer or electrospinner which can prove to be difficult or even impossible on a home-built system. Some of the commercial providers have developed systems to address this specialization aspect. The units are engineered with the option to customize the system to fit the needs of the user while maintaining all the device’s inherent features. Finding the right commercial manufacturer is key when customization is needed.
8. Service and Support
Commercial systems are usually supported by a team of expert engineers and scientists. Support on commercial units includes a range of services such as installation, training, troubleshooting, remote support, maintenance, and repair. Some commercial providers also support in developing processes for fabricating fibers or particles to meet users’ needs. Additionally, commercial systems come with a comprehensive warranty and after-sales support to handle any unforeseen issues or concerns. In contrast, home-built unit users typically rely on a narrower knowledge that exists in-house, and this can limit the application possibilities.
Summary
While home-built units can be a good initial option for proof-of-concept, commercial electrospinners are preferred instruments for research groups interested in going beyond rudimentary experiments. Researchers that need batch-to-batch consistency, quality assurance, scalability to industrial production, and adherence to cGMP practices all employ a commercial system. This enables them to fabricate high-quality fibers and particles at a high enough throughput to commercialize their electrospun or electrosprayed products. Choosing a unit should include a careful evaluation of the different commercial entities that provide these systems to ensure that they meet the user’s needs.








