Electrospinning overcomes limitations
There are multiple manufacturing processes for fiber production. Depending on the physical and/or chemical properties of the materials to be used in some techniques are more feasible than others. Common techniques include 3D printing, hot melt extrusion, and electrospinning. Among these, the electrospinning technique, which involves an electrohydrodynamic process, has attained worldwide attention to overcome some limitations from other fiber producing techniques. One example includes the ability to use thermolabile polymers and drugs during production while preventing instabilities or loss of bioactivity, as opposed to hot melt extrusion. The electrospinning technique also offers the advantage of easy fiber production from a wide range of materials and solvents.
Melt vs. Solution Electrospinning
Fiber production through electrohydrodynamic processes is typically done by melt or solution electrospinning. While melt electrospinning does not involve the use of organic solvents, it typically cannot process two, or more, polymers with different melting points at the same time without inhibiting co-polymerization. Meanwhile, solution electrospinning overcomes this disadvantage by avoiding the use of high temperatures during processing. Electrospun fibers can be easily engineered before, during and/or after the spinning process to increase fiber production.
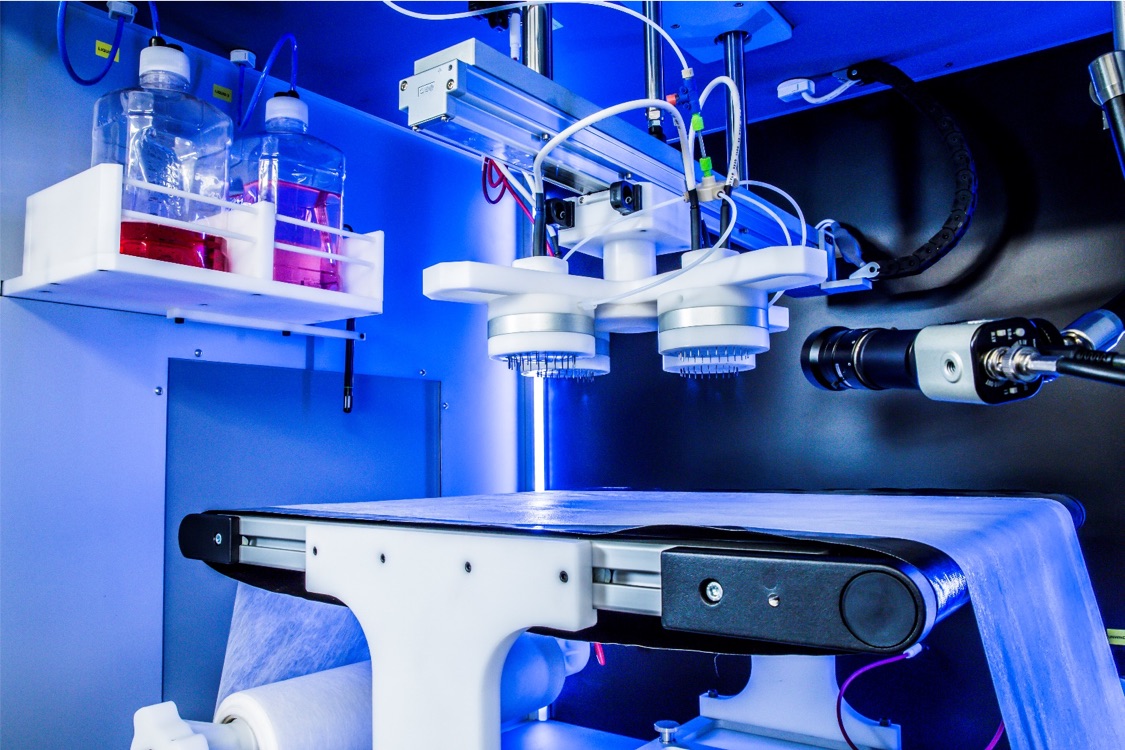
Although the electrospinning technique can be used for the production of numerous types of fibers, this process may be challenging depending on the material to be used. This technique can be assisted in various ways to either allow or improve the spinnability of the most intimidating materials. Some of these aiding processes include, but are not limited to, gas assisted electrospinning, syringe heater, climate control, Taylor cone visualization system, multi-emitters, and roll-to-roll capabilities.
In order to increase fiber production, the Fluidnatek systems can be used with multiple electrospinning heads and with a maximum of 96 emitters (LE-500) at the same time. With this, and depending on the polymeric solution used, our system has been able to produce more than 100 g/h of electrospun fibers.

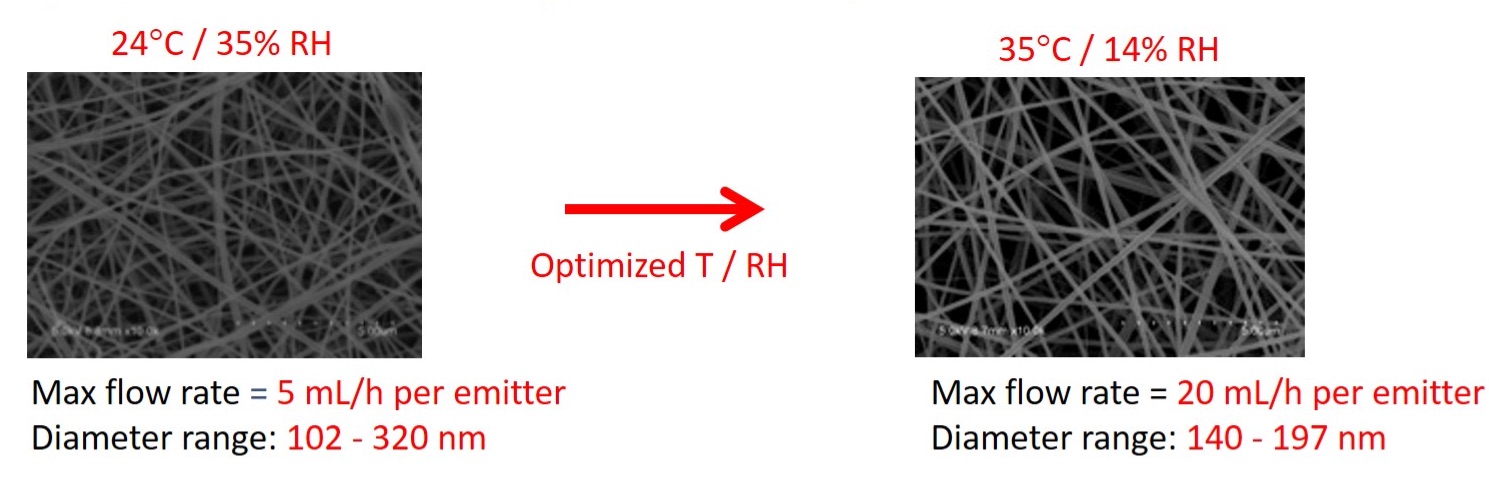
Importance of controlling temperature and relative humidity
Multiple researchers around the globe are creating fibers in locations were relative humidity and temperature vary drastically from day-to-day, month-to-month, and season-to-season. These two parameters are crucial in terms of obtaining reproducible, consistent and increased fiber production on a daily basis. The Fluidnatek units have been engineered to tightly control temperature and relative humidity during fiber production by employing an environmental control (EC) unit. With over four years of experience, our EC unit constantly conditions the air that goes into the cabin controlling the temperature from 18 to 45°C and relative humidity of 10 to 80%. This EC unit constantly removes the evaporated solvents developed from the electrospinning and electrospraying process to further maintain optimum fiber/particle production conditions.
Typical solutions to create electrospun fibers can be obtained with different concentrations and solvents. These two parameters will affect the viscosity and surface tension depending on the amount used for solution preparation. A solution with high viscosity and high surface tension is usually unable to be processed through solution electrospinning. Researchers can use external chemicals like salts to increase conductivity and decrease surface tension. This will allow the spinability of the original challenging solution by sacrificing the original unaltered solution. When the addition of new chemicals to improve the spinning process are not an option, hot solution electrospinning can be implemented. The Fluidnatek systems allow the use of a syringe heater to allow hot solution electrospinning by decreasing surface tension and improving spinability. This system can also be used in any other type of solution to decrease fiber diameter in the same way.
