In the December 2023 Edition of our QCM-D newsletter, we celebrate the first installation of a QSense Omni in the United States and highlight a variety of resources including webinars, white papers, and recent publications. You can also follow us on LinkedIn for the latest updates on QCM-D applications, events, and more!

CUSTOMER SHOWCASE
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory:
1st QSense Omni Installed in the United States
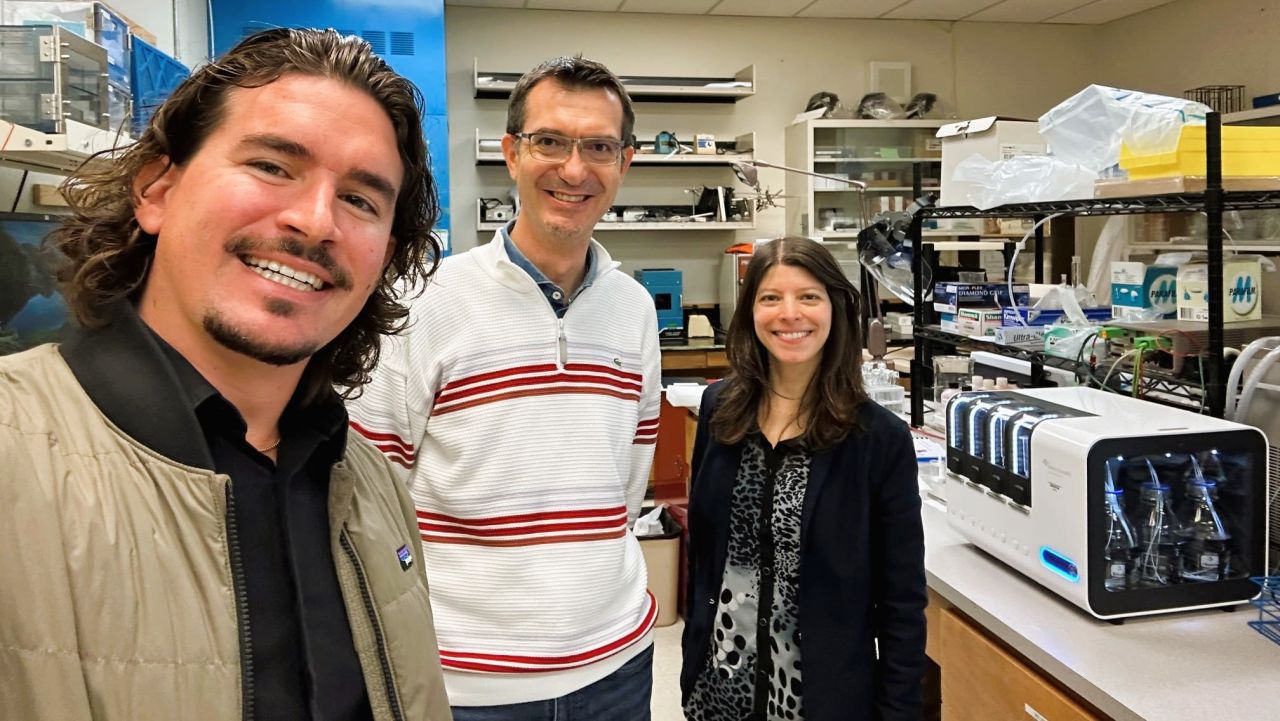

The new QSense Omni QCM-D provides unparalleled sensitivity for measuring molecular interactions at the nanoscale, enabling Dr. Francesco Fornasiero’s group at Lawrence Livermore National Lab to perform real-time, in situ quantification of ion intercalation into various materials, including polymers.
Their new 4-channel QCM-D will also support the development of next-generation breathable fabrics for a multi-institutional project sponsored by several government agencies.
Sandia National Laboratories:
Expanding QCM-D Capabilities with High-Throughput Automation
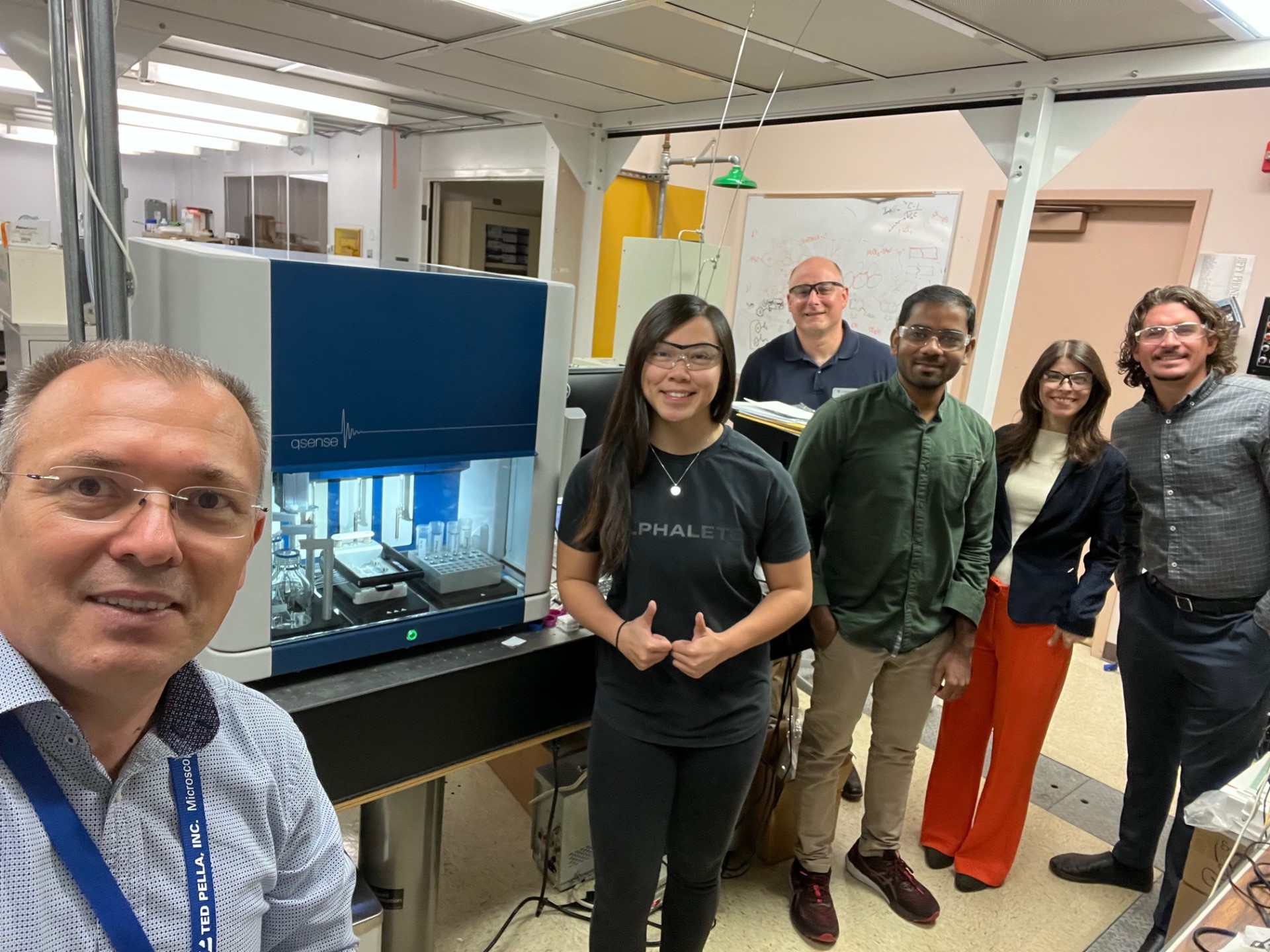

Dr. Vitalie Stavila has been a dedicated QSense user for over 10 years, leveraging a QSense Analyzer to investigate metal organic framework (MOF) molecular interactions.
His group at Sandia National Laboratoties recently upgraded to the QSense Pro, a fully-automated QCM-D engineered for high-throughput experiments.

APPLICATION UPDATES
New Application Note:
Overcoming Obstacles in Food Science with QCM-D
In this new application note, we explore how QCM-D is a valuable tool for characterizing and quantifying the molecular interactions that define the quality, appearance, safety, and sensory characteristics of foods products and food ingredients.
What you will learn about:
- Optimization of aesthetics, flavor, and sensory characteristics of food ingredients/products
- Studying fouling under high temperature & high pressure to simulate dairy processing
- Comparative assessment of processing equipment detergents
- Detecting toxins during production and improving packaging materials

WEBINARS
QCM-D Technology: From Fundamental Membrane Biophysics to Translational Applications
The quartz crystal microbalance-dissipation (QCM-D) technique has emerged as one of the most powerful bioanalytical tools to characterize biological phenomena, especially at lipid membrane interfaces. In recent years, QCM-D technology …
Key takeaways from the webinar include:
- Basics of QCM-D technology, measurement principle, and readouts
- Why label-free measurements are beneficial in the areas of biotechnology and biophysics, and what measurement capabilities QCM-D offers
- How QCM-D is used in fundamental and applied research in the areas of interfacial science, biophysics, and biotechnology
Assessing the Inflammatory Responses Induced by Biomaterials in Contact with Human Blood Using In Vitro Assays Including QCM-D
Biomaterials and nanoparticles (NPs) are used in a wide range of different health care applications from implants to dialysis membranes and cell carriers. Important for all types of biomaterial implants …
You will learn how QCM-D was used to study the biocompatibility of biomaterials by evaluating:
- Surface modifications: Anti-fouling and Regulators
- Protein – surface interactions: Surface concentration, Conformation, and Function/Activity
- Protein – protein interactions: Complex formation, Activity, and Affinity
CONFERENCE CORNER
Meet us in San Francisco for the 245th ECS Meeting!
RECENT PUBLICATIONS
Catch up on the latest research utilizing QCM-D in a variety of application areas, including pharmaceutical formulations, PFAS sorption, food science & processing, nanofiltration, and more.
If you would like to have your research featured in our next newsletter, please send us the link to your journal article!
- Quartz Crystal Microbalance as a Predictive Tool for Drug-Material of Construction Interactions in Intravenous Protein Drug Administration: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2023.07.019
- Ultra-high capacity, multifunctional nanoscale sorbents for PFOA and PFOS treatment: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-023-00263-9
- Assessing the scalability of the High-Pressure High-Temperature Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (HPHT QCM-D) for Milk Fouling Studies: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsfoodscitech.3c00131
- A new class of “structure by design” polymer membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration with controllable selectivity: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2023.122296
- Supported Erythrocyte Membranes on Piezoelectric Sensors for Studying the Interactions with Nanoparticles: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02396
- The pre-addition of “blocking” proteins decreases subsequent cellulase adsorption to lignin and enhances cellulose hydrolysis: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128276
- Significance of Co-ion Partitioning in Salt Transport through Polyamide Reverse Osmosis Membranes:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c09772