The use of energy storage systems, such as Li-ion batteries, has significantly increased in recent decades, on both the grid-scale and individual consumer levels. With the global shift to renewable energy, such as wind and solar power, the need for energy storage will continue to rise. Researchers are trying to optimize efficiency, cost, and environmental impact of these devices.
Batteries and fuel cells are commonly used energy storage systems. Due to their low cost and high energy density, Li-ion batteries represent one of the most commercially viable storage options. The performance and life span of these devices heavily depend on the materials chosen, and the electrochemical reactions occurring at the electrode surfaces.
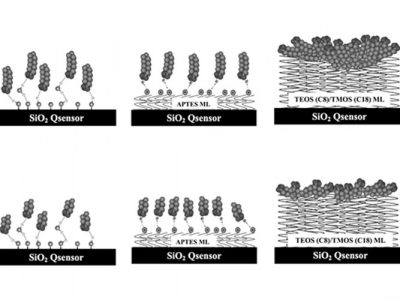
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D), being an extremely surface sensitive technique, has been used at different stages of research related to energy storage systems. Examples include, characterization of electrode materials, electrode corrosion, investigation of SEI, viscoelasticity of interfacial films, and Hydrogen uptake by thin films.
Join Dr. Archana Jaiswal for our free webinar where she will highlight the use of both QCM-D and electrochemical QCM-D (EQCM-D) in battery, fuel cell and Hydrogen uptake by thin films applications.